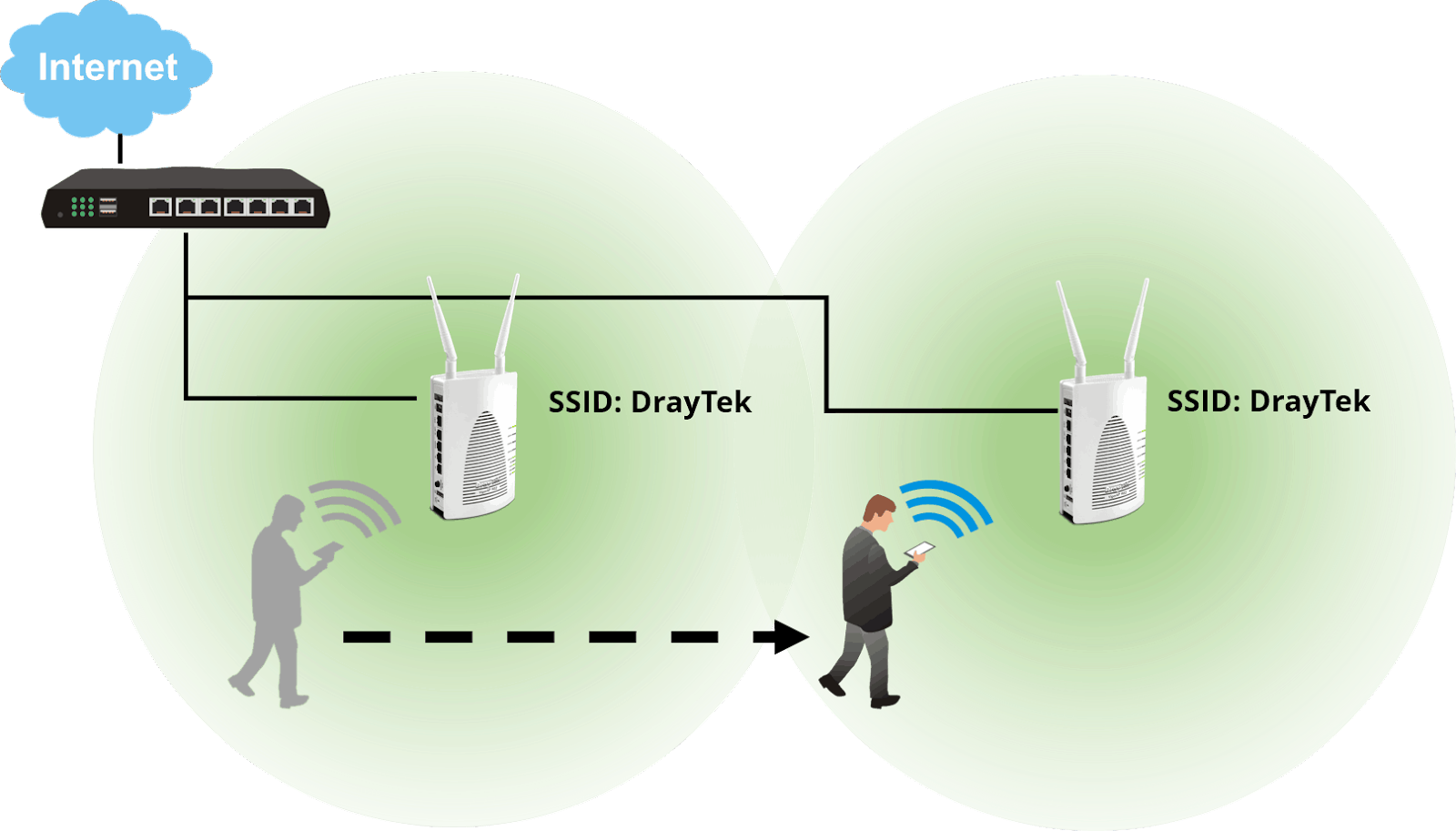
Roaming 802.11k/v/r
📍802.11𝐤 – 𝐍𝐞𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐛𝐨𝐫 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐬𝐭/𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐩𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐞.
✓When the client wants to find a better network to connect to, it sends its current AP a Neighbor report request frame.
✓The current AP then sends a neighbor report response that will contain a list of all the candidate neighboring APs along with their capabilities.
ℹ️ 𝐍𝐞𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐛𝐨𝐫 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐩𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐞 𝐈𝐧𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐄𝐥𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬:
> BSSID: MAC address of the target AP
> BSSID Info: Capabilities of the target AP
> Operating Class: Channel Set of the AP based on operating country.
> Channel Number: Channel of target AP.
> PHY Type: PHY details of the target AP.
> Sub elements: Other vendor specific elements.
✓The client can then select from the list the AP it wants to connect to and then send go through the connection process with the new AP.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐢𝐭 𝐇𝐞𝐥𝐩𝐬?
✓Always finding the best network available to connect
Making the search for a new AP much easier when its time to roam.
✓Removes the need for moving off the current channel to find other networks.
✓Much more efficient usage of the medium by reducing the amount of on air frames.
📍802.11𝐯 – 𝐁𝐒𝐒 𝐓𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐌𝐚𝐧𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭 #80211v
BSS transition management (BTM) enables clients to roam to the optimal AP if the signal strength of the current AP is low or if a better AP is discovered.
☑️ 𝐁𝐓𝐌 𝐨𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐬 𝐚𝐬 𝐟𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐬:
✓The AP or the 802.11v client triggers a BSS transition:
> 𝐔𝐧𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐫𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐬𝐭 : If the AP detects that the RSSI of the client is lower than the RSSI threshold, it sends a BTM request to the client.
> 𝐒𝐨𝐥𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐫𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐬𝐭 : If the RSSI of the currently associated AP is too low or the client discovered a better AP, the client sends a BTM query to the associated AP. Upon receiving the query, the AP responds with a BTM request.
✓A BTM request contains information about recommended BSSs.
✓Upon receiving the BTM request, the client determines whether to disconnect from the current AP and roam to a recommended AP.
✓If the client determines to perform a roaming, it sends a BTM response to the AP. If the client fails to leave the current BSS before the disassociation timer expires, the AP sends a disassociation request to the client and logs off the client.
📍802.11𝐫 – 𝐅𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐁𝐒𝐒 𝐓𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 🚀
IEEE 802.11r introduces a new concept of roaming where the initial handshake with the new AP is done even before the client roams to the target AP, which is called Fast Transition (FT).
The initial handshake allows the client and APs to do the Pairwise TransientKey (PTK) calculation in advance. These PTK keys are applied to the client and AP after the client does the reassociation request or respons exchange with new target AP.
For a client to move from its current AP to a target AP using the FT protocols,
The message exchanges are performed using one of the following two methods:
✓𝐎𝐯𝐞𝐫-𝐭𝐡𝐞-𝐀𝐢𝐫 : The client communicates directly with the target AP using IEEE 802.11 authentication with the FT authentication algorithm.
✓𝐎𝐯𝐞𝐫-𝐭𝐡𝐞-𝐃𝐒 : The client communicates with the target AP through the current AP. The communication between the client and the target.
AP is carried in FT action frames between the client and the current AP and is then sent through the controller.



Comments
Post a Comment